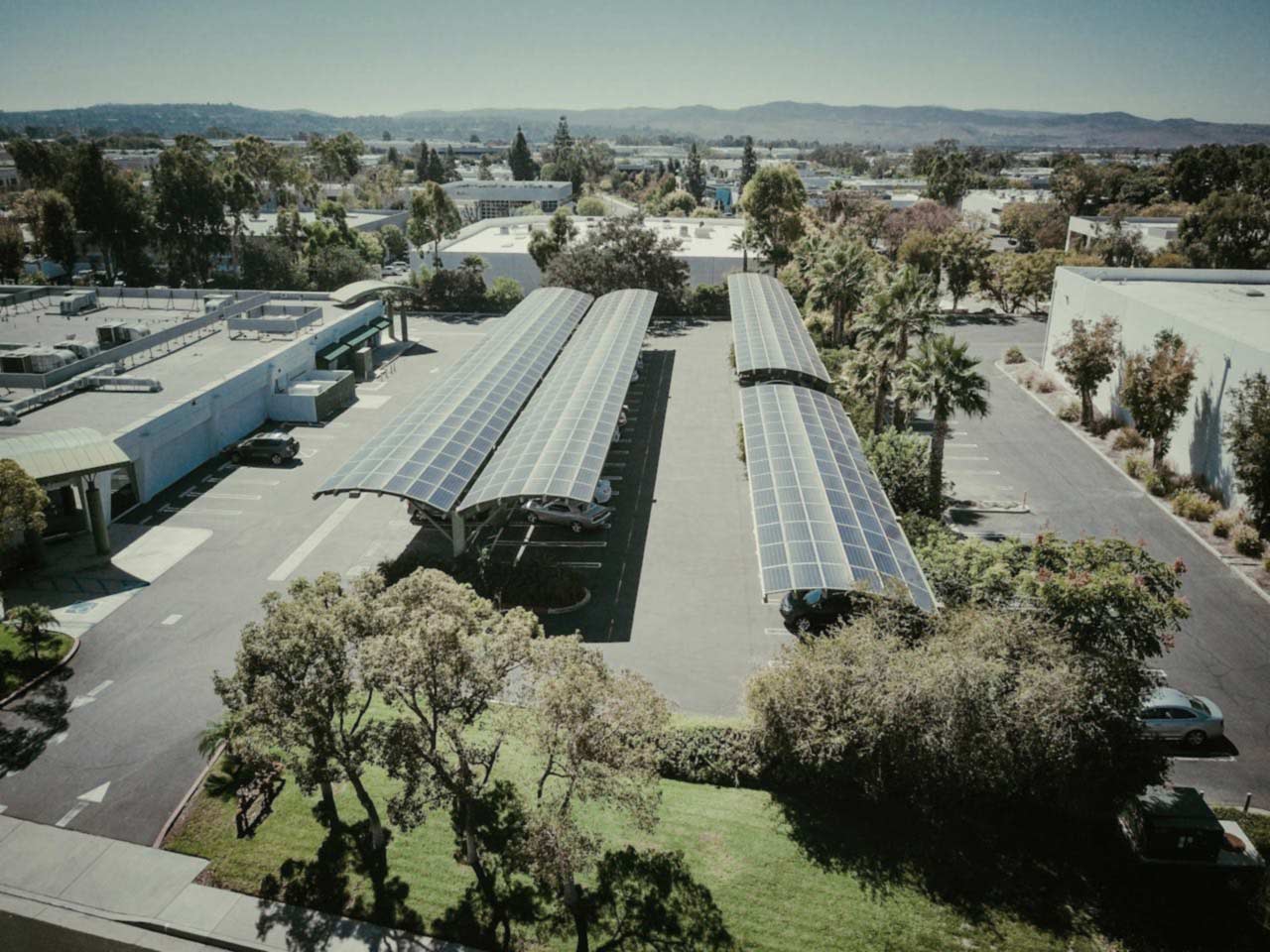
Among the advantages of using solar to power your business needs is the independence achieved from grid energy storage. However, in order to maximise independence from the grid, storing the excess energy generated by your solar plant presents another way to consume the energy generated by your plant.
The advantage of energy storage is that it allows for power harvesting at a steady rate. If the demand for power is low, the excess energy generated by your solar plant is stored in batteries. At times when the power requirement exceeds power generation at that particular instance of time, power can be drawn from the power batteries. This cycle keeps the system entirely independent of the grid.
There are several battery technologies prevalent in the market today. Some of the dominant battery-types are examined here:
Lead Acid Battery: The oldest rechargeable battery, the lead-acid has a wide range of uses because of its tried and tested reliability.
This battery type has emerged at the forefront of the energy storage industry, backed by the expanding EV segment.
NICAD (Nickel-Cadmium): The NICAD battery is an alkaline battery where an alkaline solution acts as the electrolyte of the system. Despite its higher levels of rechargeability, the NICAD does not have a measurable presence in the energy storage market for renewables due to its high cost and difficulty of disposal due to the toxic substances present in the system.
The above batteries are all susceptible to inflicting fire breakouts.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion): The Li-ion battery has often featured in news pieces for having triggered fires. Another common disadvantage among conventional batteries is the presence of toxic substances used in, and created during, the energy-storage chemical cycle. This not only creates additional disposal costs for the business, but is also detrimental to the ecosystem at large.
It is against this background that we turn to salt water batteries, the batteries with the potential to revolutionize energy storage.
What is a salt water battery?
A salt water battery is a battery where alkali-ion salt water acts as the electrolyte of the system. The anode is a carbon titanium phosphate composite, while the cathode used is Manganese Oxide. Synthetic cotton is used as a separator. A variation of the above system uses a mixture of manganese sulphate and water as an electrolyte and manganese oxide as an electrolyte.
The Benefits of a Salt Water Battery
Eco-Friendly and Safe:
The presence of salt water in the system immediately eliminates any fire hazards and also allows for recycling, making it a far more environmentally and business-friendly battery alternative to conventional batteries.
No Thermal Runaway Risk:
Batteries are usually required to be operated at fixed temperature windows. As batteries are recharged, they heat up. Now, if due to this heat, the operating temperature increases sufficiently to cross the threshold, it would result in thermal runaway. In thermal runaway, the rise in temperature is continuously compounded as the external heat forces the battery to heat the battery up further as it operates. This cycle continues, and if not checked, would cause the battery to heat up to temperatures that would spark a fire—which could have catastrophic impacts on the entire plant. The chemistry of a salt-water battery brings this risk down to nil.
Cost Advantages:
As saltwater and MnO form the main components of the saltwater battery, the cost of the device would also be far less than its alternatives. However, the drop in price is subject to a rise in production of these batteries. As saltwater batteries are still at a nascent stage of entering the market, costs are not currently at levels deemed efficient for active usage in the renewable industry.
Long lifecycle: As compared to the current dominant players in the battery industry, the saltwater battery has a long lifecycle of over 10,000 cycles of charge and discharge, which translates to a decade of use, before it begins to display signs of degradation.
Resilient: Saltwater batteries are more resilient as they are less vulnerable to temperature swings and can operate in a wide window of temperatures, from -5 to 40 degrees Celsius. This allows them to hold steady performance and efficiency values.
As we progress towards a more solarised world than ever before, the battery energy storage system industry will, in the coming years, grow to match the renewable industry stride for stride.
The Future of Sustainable Energy Storage
As solar adoption rises, the need for safe and reliable battery energy storage systems will grow in parallel. Salt Water Batteries are poised to meet this demand, offering a sustainable, safe, and long-lasting energy solution.
FAQs: Salt Water Batteries for Eco-Friendly Energy Storage
What are salt water batteries and how do they work?
Salt water batteries use a saline (salt-based) solution as the electrolyte, along with non-toxic materials like carbon titanium phosphate and manganese oxide. These components enable safe and efficient energy storage without the fire risks or toxic waste associated with traditional batteries.
Are salt water batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
Yes, salt water batteries are much safer. They do not carry the risk of thermal runaway or fire, which is a common concern with lithium-ion batteries. Their non-flammable chemistry makes them ideal for eco-conscious and risk-averse energy storage needs.
Can salt water batteries be used for solar energy storage?
Absolutely. Salt water batteries are a great match for solar systems. They store excess solar power during the day and release it when needed, making them an effective solution for off-grid or grid-independent solar applications.
How long do salt water batteries last?
Salt water batteries offer a long lifecycle—typically over 10,000 charge-discharge cycles, which can translate to more than a decade of consistent use with minimal degradation.
Are salt water batteries environmentally friendly?
Yes, salt water batteries are considered one of the most eco-friendly energy storage options. They are non-toxic, recyclable, and do not produce hazardous waste, making them an ideal choice for businesses focused on sustainability.