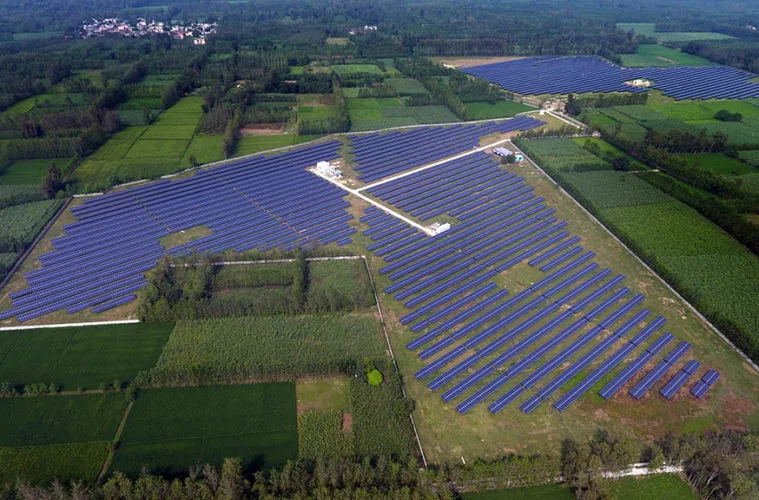
Ground Mounted solar installations conjure up an image of large swathes of land dominated by the strong dark blue of solar modules, powering businesses, factories, and sustainable growth. As the appetite for solar energy grows in India, we see several landowners warming up to the idea of installing ground-mounted solar plants on their land to raise their savings and enter into PPAs. In the race to solarize our lands, the utility market has shot far ahead, standing atop the leaderboard.
Progressing from Ideation to Actuation
As with all solar installations, in ground-mount solar powered plants, the size of the project, the tilt of the modules, as well as the site-specific technical specifications of cable lengths, locations and capacities of inverters, LT & HT panels, among other project intricacies, are directly decided by the design engineers involved in the project. These design factors are considered by the design and engineering team when a detailed study of the site is carried out.
When a ground-mounted solar project kicks off, the project passes through a certain number of definitive phases that dictate the speed and efficiency with which the project is readied for commission.
- Once the installation site has been allocated and the power consumption needs of the user have been determined, a detailed site survey is carried out by the solar EPC firm that is likely to carry out the complete installation.
- During the site visit, the project’s design and engineering team takes into account all of the site’s characteristics, including the land’s levelling requirements, to create the design of the solar power plant project.The ideal design is a perfect amalgamation of customer requirements and site realities. A solar installation design uses the details of the required plant capacity with the electrical components, modules, and physical structures, among other nitty-gritties.
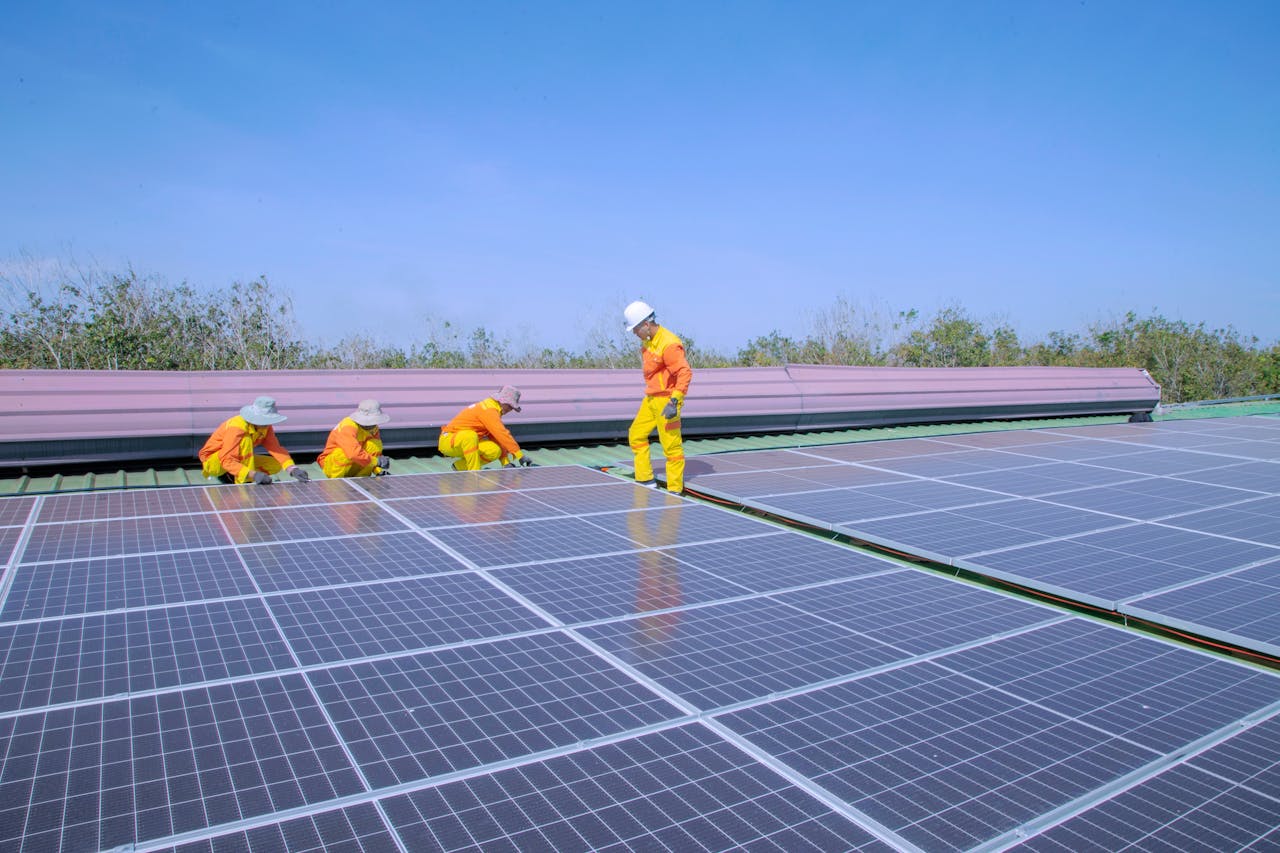
- Once approved, the engineering designs are handed over to the project team that employs labour and materials to complete the project, delivering it to the client within the time and cost heads previously agreed upon.
- Regular cleaning of the panels and checks on the growth of plants or the creation of shading obstacles are all small minute details which, if left unattended, would reduce the efficiency of the solar plant and, ultimately, energy generation.
Also Read: Module Mounting Structures for Ground Mount Solar Installations
Maximizing Efficiency in Ground-Mounted Solar Installations
Efficiency can be discussed via various different prisms: of the modules, the electrical components, and the design, among a few others. Harmonising methods that maximise efficiency, along with the broad processes that are involved in installation, presents the opportunity to envision a truly complete solar installation. Here, we cast a brief eye on a few instances of design and technology working in tandem to raise this very efficiency.
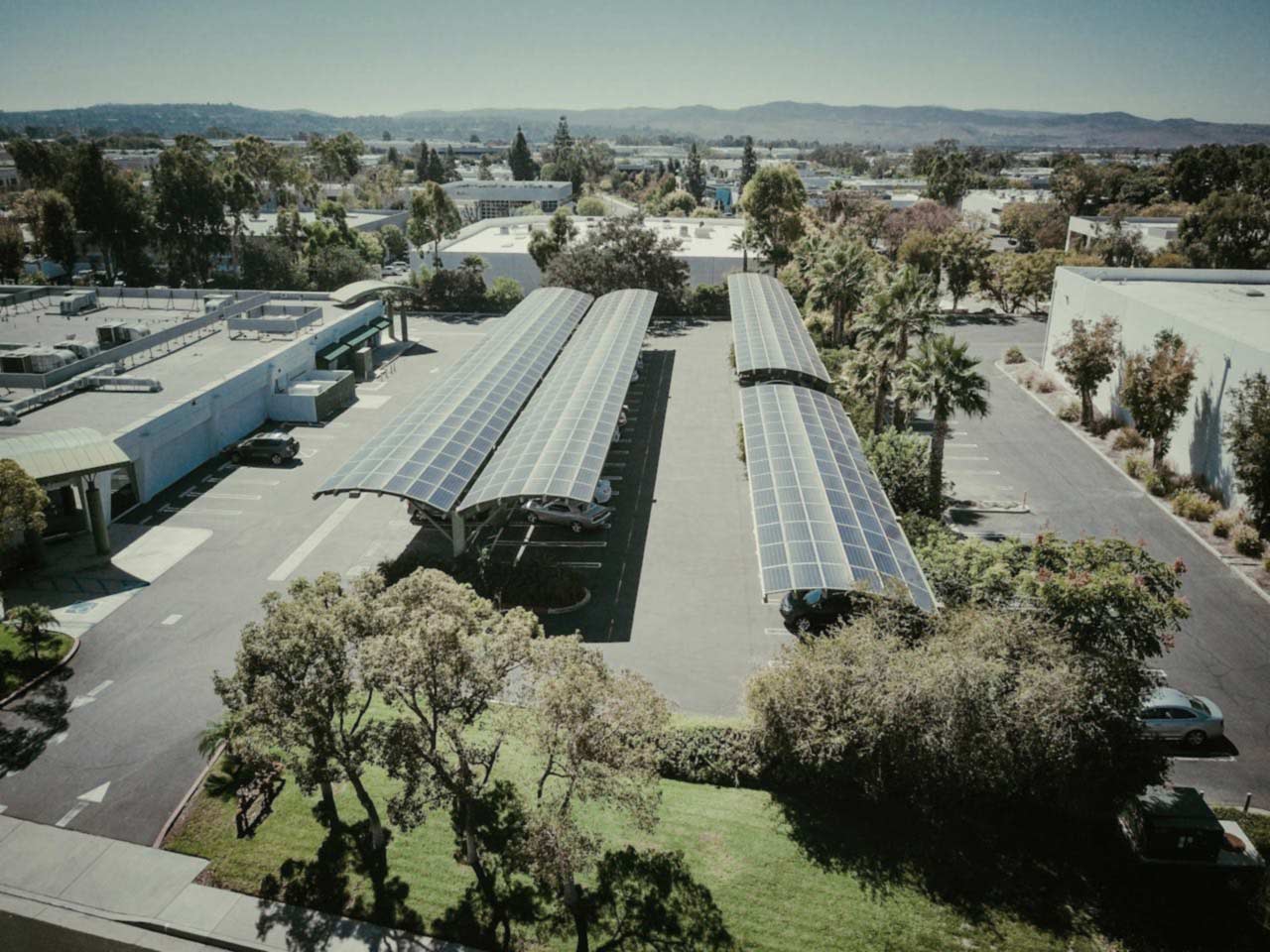
Module Canopies
This type of installation is ideal to maximise the usage of land on which a ground mounted solar panels installation is carried out. Modules are installed in the form of canopies, i.e., they are raised significantly above the surface of the ground, allowing the space under the modules to be used. For instance, carports are systems where the space below the module canopies is used as parking spaces.
Conventional systems
These are the most commonly found systems wherein ramming or a pile foundation may be employed to affix the weight-bearing structure to the ground. The support structure thus formed bears the weight of the module as well as the back support of the module. The back support of the modules is designed so as to clasp the modules at the designed tilt angle. Arriving at the right type of foundation for the installation is a critical part of the design as it dictates the stability of the installation.
Tracking systems
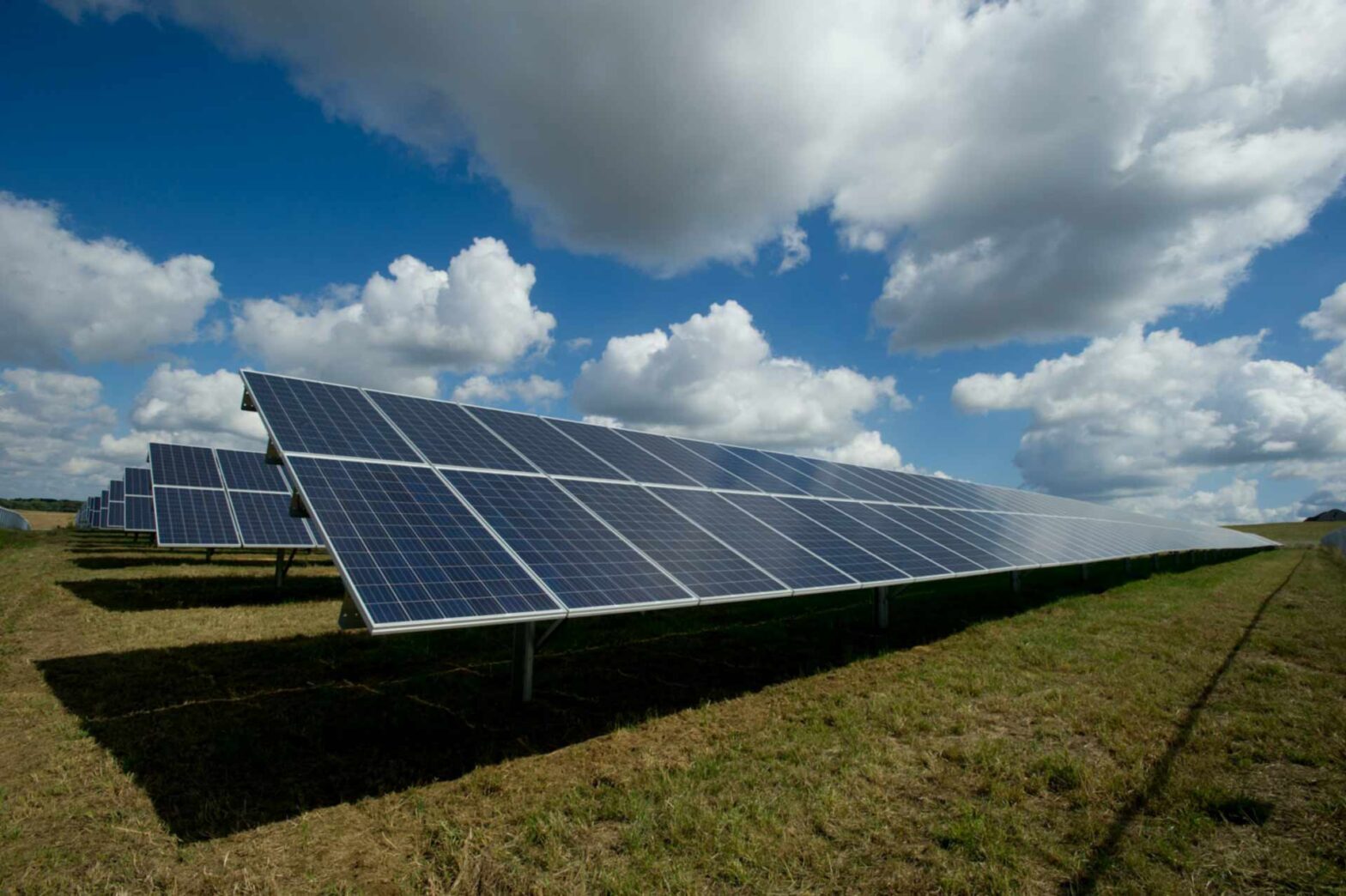
In several solar installations today, the modules are fitted with single-axis or dual-axis trackers that allow the modules to move about their clamps, along the arc of their tilt angle, to follow the movement of sunlight during the day.
Ground-mounted solar power plants are thus not only hugely important investments in clean energy, but they also generate savings for businesses, require minimal maintenance, and drastically reduce the operational costs of large power consumers, securing sustainable growth for future successes.